The Cost of Overwatering in Mining Dust Suppression
Water consumption for dust suppression represents one of the largest non-processing water uses in mining operations, often accounting for 30-50% of total site water consumption. Many operations still rely on scheduled watering routines—spraying roads, stockpiles, and work areas at predetermined intervals regardless of actual dust conditions or weather patterns.
This reactive approach creates significant waste. Water trucks may spray areas that don't require suppression, oversaturate surfaces that become muddy and unworkable, or fail to target emerging dust sources before they become compliance issues. The financial implications are substantial: excess water consumption increases procurement costs, pumping expenses, and treatment requirements, whilst operational inefficiencies compound these losses.
From an ESG perspective, overwatering undermines sustainability commitments and community relations. In water-stressed regions, excessive consumption for dust control can strain local resources and create stakeholder tensions. Meanwhile, inadequate dust management poses serious health and safety risks, regulatory compliance challenges, and potential community impact concerns.
Smarter Dust Control Starts with Smarter Data
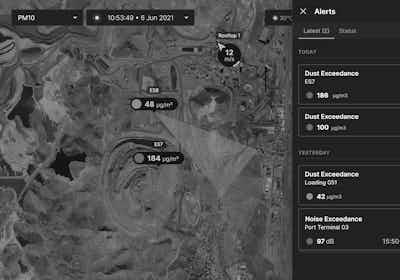
Effective dust management requires understanding when, where, and how much dust will be generated before it becomes a problem. Modern dust monitoring systems provide continuous, real-time data from multiple monitoring points across mine sites, creating a comprehensive picture of dust behaviour patterns.
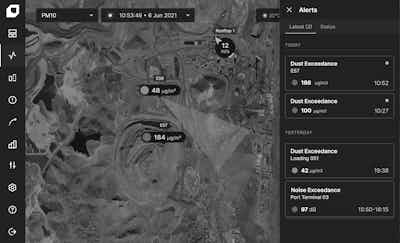
This data becomes truly powerful when combined with meteorological forecasting and predictive modelling. By understanding wind patterns, atmospheric stability, humidity levels, and operational schedules, mining teams can predict dust generation potential hours or even days in advance. Real-time monitoring validates these predictions and triggers targeted suppression actions only when and where needed.
Smart alert systems transform this information into actionable insights. Rather than following rigid watering schedules, operations can receive automated notifications when dust levels approach predetermined thresholds, enabling proactive intervention before compliance limits are breached. This approach shifts dust management from reactive crisis response to strategic operational planning.
Weather integration proves particularly valuable. High humidity conditions naturally suppress dust, reducing or eliminating the need for water application. Conversely, dry, windy conditions may require increased suppression in specific areas whilst leaving others untouched. This nuanced understanding prevents both under-suppression and overwatering.
Operational and Environmental Benefits of Data-Driven Dust Suppression
Intelligent dust monitoring delivers measurable improvements across multiple operational dimensions. Water use efficiency increases dramatically when suppression efforts target actual dust generation rather than predetermined schedules. Many operations report 20-40% reductions in water consumption whilst maintaining or improving dust control effectiveness.
Operational efficiency gains extend beyond water savings. Targeted suppression reduces mud formation, maintaining road conditions that support faster vehicle transit and reduced tyre wear. Equipment operators work in improved visibility conditions, enhancing safety and productivity. Water truck scheduling becomes more efficient, reducing fuel consumption and equipment wear whilst enabling better deployment of resources to genuine priority areas.
Compliance confidence strengthens significantly with continuous monitoring and predictive capabilities. Rather than hoping scheduled watering will prevent exceedances, operations can demonstrate proactive dust management with documented evidence of real-time responses to changing conditions. This approach supports regulatory reporting requirements whilst reducing the risk of unexpected compliance issues.
Environmental and community benefits compound these operational improvements. Reduced water consumption supports broader sustainability objectives whilst demonstrating responsible resource stewardship. More effective dust control protects air quality for both workers and surrounding communities, supporting social licence to operate and ESG reporting requirements.
The Path Forward for Intelligent Dust Monitoring
The integration of intelligent dust monitoring with water management represents a fundamental shift from wasteful reactive practices to efficient proactive strategies. By leveraging real-time data, predictive modelling, and smart alert systems, mining operations can achieve superior dust control whilst significantly reducing water consumption.
This approach delivers compelling returns on investment through reduced water costs, improved operational efficiency, enhanced compliance confidence, and stronger ESG performance. As water scarcity increases and environmental expectations intensify, data-driven dust management becomes not just an operational improvement but a strategic necessity.
Ready to revolutionise your dust management strategy?
Contact Envirosuite today to discover how intelligent dust monitoring can help your operation reduce water waste whilst maintaining operational control and compliance. Our team can demonstrate how real-time data and predictive insights deliver measurable improvements in both dust control effectiveness and water use efficiency.